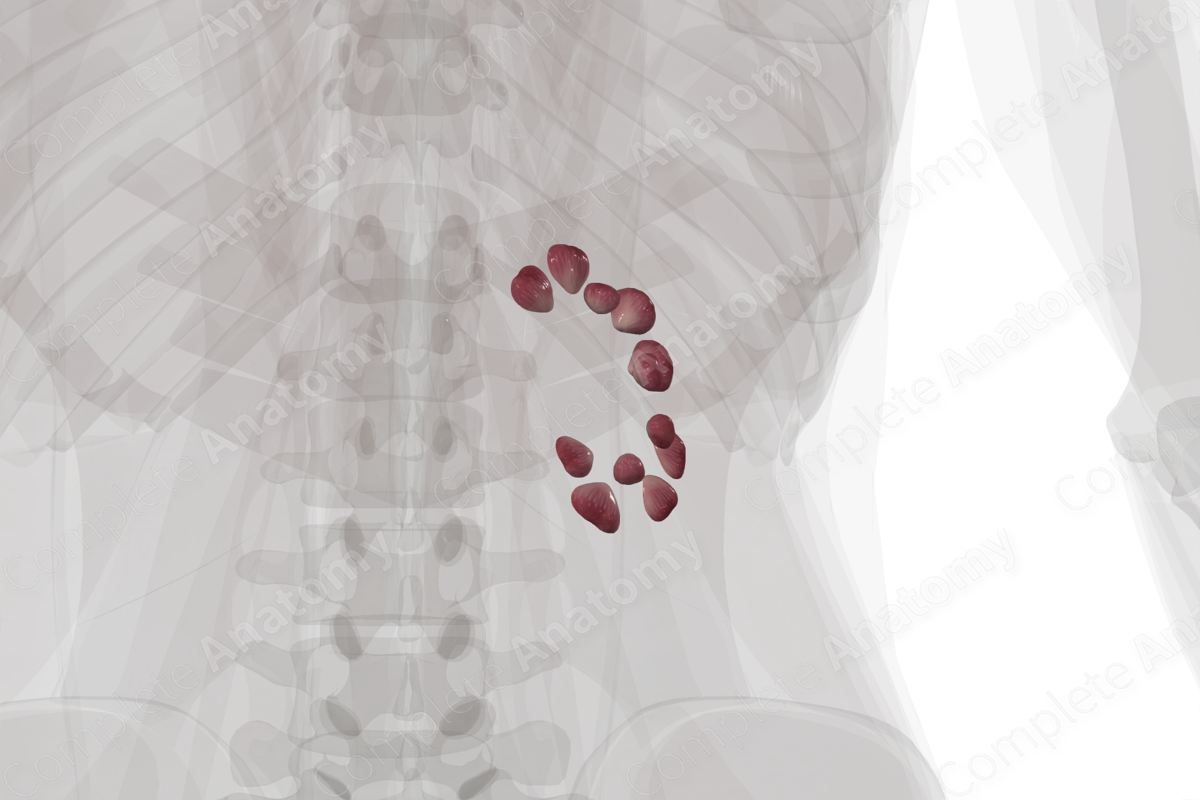
Renal Medulla (Anterior Part; Left) Structure/Morphology
The renal medulla predominately consists of the renal pyramids that are separated from each other by the renal columns.
Related parts of the anatomy
Renal Medulla (Anterior Part; Left) Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The renal medulla is the inner portion of the kidney located deep to the renal cortex.
Renal Medulla (Anterior Part; Left) Function
The majority of the nephron loop (of Henle) travels through the renal medulla, which is responsible for the majority of water reabsorption, making urine hypertonic. The vasa recta (straight vessels) surround the loop of Henle aiding in the countercurrent exchange, which allows for the concentration of urine.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Renal Medulla

papillary d’s (kidney) the straight excretory or collecting portions of the renal tubules, which descend through the renal medulla to a renal papilla or renal crest.




