Structure/Morphology
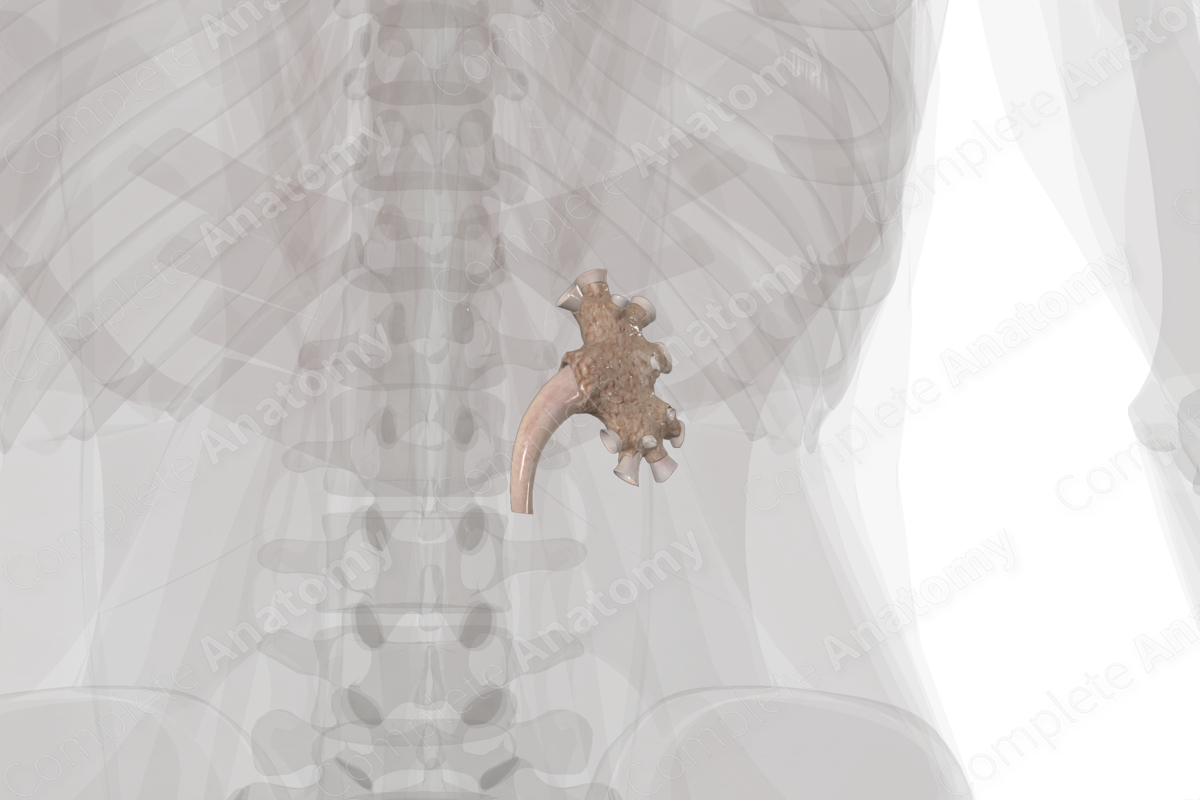
The renal sinus is a cavity filled with fat, blood vessels, nerves, renal calices, and the renal pelvis.
Related parts of the anatomy
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The renal sinus is located along the medial surface of the kidney.
Function
The renal sinus is the continuation into the kidney from the renal hilum and represents the entire collecting portion of the urinary system, which includes the minor calices, major calices, and the renal pelvis. The sinus also contains the renal vessels as they branch to enter the renal tissue as the renal arteries or converging to exit the kidneys as the renal veins.
List of Clinical Correlates
—Kidney stones
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





